
The lab’s research spans every aspect of battery development, from the breakthrough fundamental science of the Argonne-led Joint Center for Energy Storage Research, a DOE Energy Innovation Hub, to the Argonne Collaborative Center for Energy Storage Science, a cross-lab collective of scientists and engineers that solves complex battery problems through multidisciplinary research.Īrgonne researchers are also exploring how to accelerate the recycling of lithium-ion batteries through the DOE’s ReCell Center, a collaboration led by Argonne that includes the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, as well as Worcester Polytechnic Institute, University of California at San Diego and Michigan Technological University.įor another take on “Batteries 101,” check out DOE Explains.

automotive fleet toward plug-in hybrid and electric vehicles, and enabled greater use of renewable energy, such as wind and solar power.
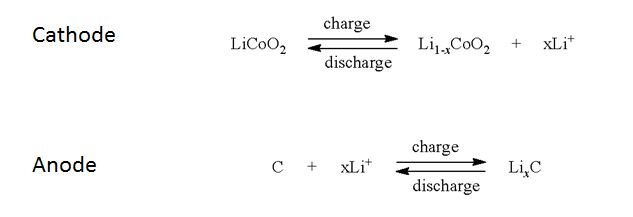
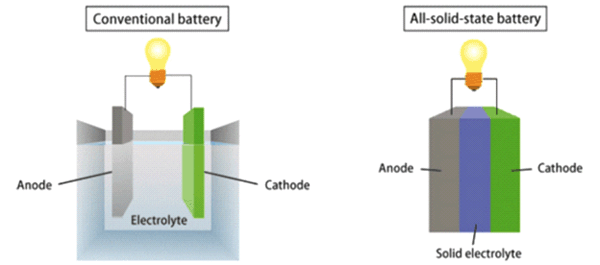
battery manufacturing industry, aided the transition of the U.S. Over the past sixty years, the lab’s pivotal discoveries have strengthened the U.S. Department of Energy’s ( DOE) Argonne National LaboratoryĪrgonne is recognized as a global leader in battery science and technology. Since this cycle can be repeated hundreds of times, this type of battery is rechargeable. This provides the energy to keep your devices running. When you plug in your cell phone to charge the lithium-ion battery, the chemical reactions go in reverse: the lithium ions move back from the cathode to the anode.Īs long as lithium ions shuttle back and forth between the anode and cathode, there is a constant flow of electrons. Chemical reactions occur that generate electrons and convert stored chemical energy in the battery to electrical current. When a lithium-ion battery is turned on, positively charged particles of lithium (ions) move through the electrolyte from the anode to the cathode. All provide an initial voltage of 1.55 to 1.7 volts, which declines with use to an end point of about 0.8 volt. There are three variations: the zinc-carbon battery, the zinc chloride battery, and the alkaline battery. Lithium-ion batteries that power cell phones, for example, typically consist of a cathode made of cobalt, manganese, and nickel oxides and an anode made out of graphite, the same material found in many pencils. These batteries are the most commonly used worldwide in flashlights, toys, radios, compact disc players, and digital cameras.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
